Short circuit current calculation.
Purpose
It plays a very important role to protect & also safety of commercial and industrial electrical equipment like circuit breakers,transformers …etc.
What is short circuit current?
When two or more conductors are different phases come in contact with each other in a line, transformer or any other power element, then the part of the impedance is shunted out of the circuit due to which a large current flow in the un-faulted phases, such current is called the short circuit current.
It reduces the effect of impedance in the circuit while the current in the circuit rises.
- The flow of large current will overheat the equipment.
- The flow of short circuit current in the current carrying parts produces a force of electrodynamics interaction which may destroy or damage the equipment.
Fault MVA = (Base MVA / % Z ) × 100
MVA = KVA / 1000
Where,
Base MVA= Transformer Rating
%Z = Impedance + 10 % tolerance of z
Isc =Fault MVA / (√3 × Base KVA )
Where,
I SC = Value of fault current or short circuit current in KA
Base KVA= Transformer is secondary output voltage (like 6.6kv/440 v)
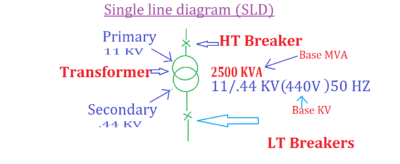
So let’s take Quick Observation
Calculate Fault current at each stage of following Electrical System SLD having details of.
- Transformer Rating is 2.5 MVA.
- Transformer Impedance is 7.25 %.
Solution:
Use the above formula to convert MVA to KVA
2500/1000= 2.5 MVA
As per above formula
Fault MVA =2.5 / (7.25 % + 10% tolerance) × 100
= 2.5 / (7.25 +0.725) × 100
=31.32 MVA
Now calculate Short circuit current
Isc = 31.32 / (√3 × 0.44) = 41.09 KA
Short circuit current is 41.09 KA.
How to calculate Voltage drop ?
How to calculate transformer sizing ?
